Contents
- Healthcare Infrastructure
- Graphs
- Healthcare Facilities and Services
- A. Public and Govt-Aided Medical Facilities
- B. Private Healthcare Facilities
- C. Approved vs Working Anganwadi
- D. Anganwadi Building Types
- E. Anganwadi Workers
- F. Patients in In-Patients Department
- G. Patients in Outpatients Department
- H. Outpatient-to-Inpatient Ratio
- I. Patients Treated in Public Facilities
- J. Operations Conducted
- K. Hysterectomies Performed
- L. Share of Households with Access to Health Amenities
- Morbidity and Mortality
- A. Reported Deaths
- B. Cause of Death
- C. Reported Child and Infant Deaths
- D. Reported Infant Deaths
- E. Select Causes of Infant Death
- F. Number of Children Diseased
- G. Population with High Blood Sugar
- H. Population with Very High Blood Sugar
- I. Population with Mildly Elevated Blood Pressure
- J. Population with Moderately or Severely High Hypertension
- K. Women Examined for Cancer
- L. Alcohol and Tobacco Consumption
- Maternal and Newborn Health
- A. Reported Deliveries
- B. Institutional Births: Public vs Private
- C. Home Births: Skilled vs Non-Skilled Attendants
- D. Live Birth Rate
- E. Still Birth Rate
- F. Maternal Deaths
- G. Registered Births
- H. C-section Deliveries: Public vs Private
- I. Institutional Deliveries through C-Section
- J. Deliveries through C-Section: Public vs Private Facilities
- K. Reported Abortions
- L. Medical Terminations of Pregnancy: Public vs Private
- M. MTPs in Public Institutions before and after 12 Weeks
- N. Average Out of Pocket Expenditure per Delivery in Public Health Facilities
- O. Registrations for Antenatal Care
- P. Antenatal Care Registrations Done in First Trimester
- Q. Iron Folic Acid Consumption Among Pregnant Women
- R. Access to Postnatal Care from Health Personnel Within 2 Days of Delivery
- S. Children Breastfed within One Hour of Birth
- T. Children (6-23 months) Receiving an Adequate Diet
- U. Sex Ratio at Birth
- V. Births Registered with Civil Authority
- W. Institutional Deliveries through C-section
- X. C-section Deliveries: Public vs Private
- Family Planning
- A. Population Using Family Planning Methods
- B. Usage Rate of Select Family Planning Methods
- C. Sterilizations Conducted (Public vs Private Facilities)
- D. Vasectomies
- E. Tubectomies
- F. Contraceptives Distributed
- G. IUD Insertions: Public vs Private
- H. Female Sterilization Rate
- I. Women’s Unmet Need for Family Planning
- J. Fertile Couples in Family Welfare Programs
- K. Family Welfare Centers
- L. Progress of Family Welfare Programs
- Immunization
- A. Vaccinations under the Maternal and Childcare Program
- B. Infants Given the Oral Polio Vaccine
- C. Infants Given the Bacillus Calmette Guerin (BCG) Vaccine
- D. Infants Given Hepatitis Vaccine (Birth Dose)
- E. Infants Given the Pentavalent Vaccines
- F. Infants Given the Measles or Measles Rubella Vaccines
- G. Infants Given the Rotavirus Vaccines
- H. Fully Immunized Children
- I. Adverse Effects of Immunization
- J. Percentage of Children Fully Immunized
- K. Vaccination Rate (Children Aged 12 to 23 months)
- L. Children Primarily Vaccinated in (Public vs Private Health Facilities)
- Nutrition
- A. Children with Nutritional Deficits or Excess
- B. Population Overweight or Obese
- C. Population with Low BMI
- D. Prevalence of Anaemia
- E. Moderately Anaemic Women
- F. Women with Severe Anaemia being Treated at an Institution
- G. Malnourishment Among Infants in Anganwadis
- Sources
NANDED
Health
Last updated on 26 July 2025. Help us improve the information on this page by clicking on suggest edits or writing to us.
Nanded’s healthcare landscape, like many other regions across India, is shaped by a mix of indigenous and Western medical practices. For centuries, indigenous knowledge and treatments provided by practitioners such as hakims and vaidyas have formed the foundation of healthcare in the region. This long-standing relationship between communities and their natural environment played a key role in shaping the district’s early medical traditions. Over time, its landscape has gradually evolved with the introduction and expansion of more specialized medical services.
Healthcare Infrastructure
Much like other regions in India, Nanded’s healthcare infrastructure follows a multi-tiered system that involves both public and private sectors. The public healthcare system is structured into primary, secondary, and tertiary levels. Primary care is provided through Sub Centres and Primary Health Centres (PHCs), secondary care is managed by Community Health Centres (CHCs) and Sub-District hospitals, while tertiary care, the highest level, is delivered through Medical Colleges and District Hospitals.
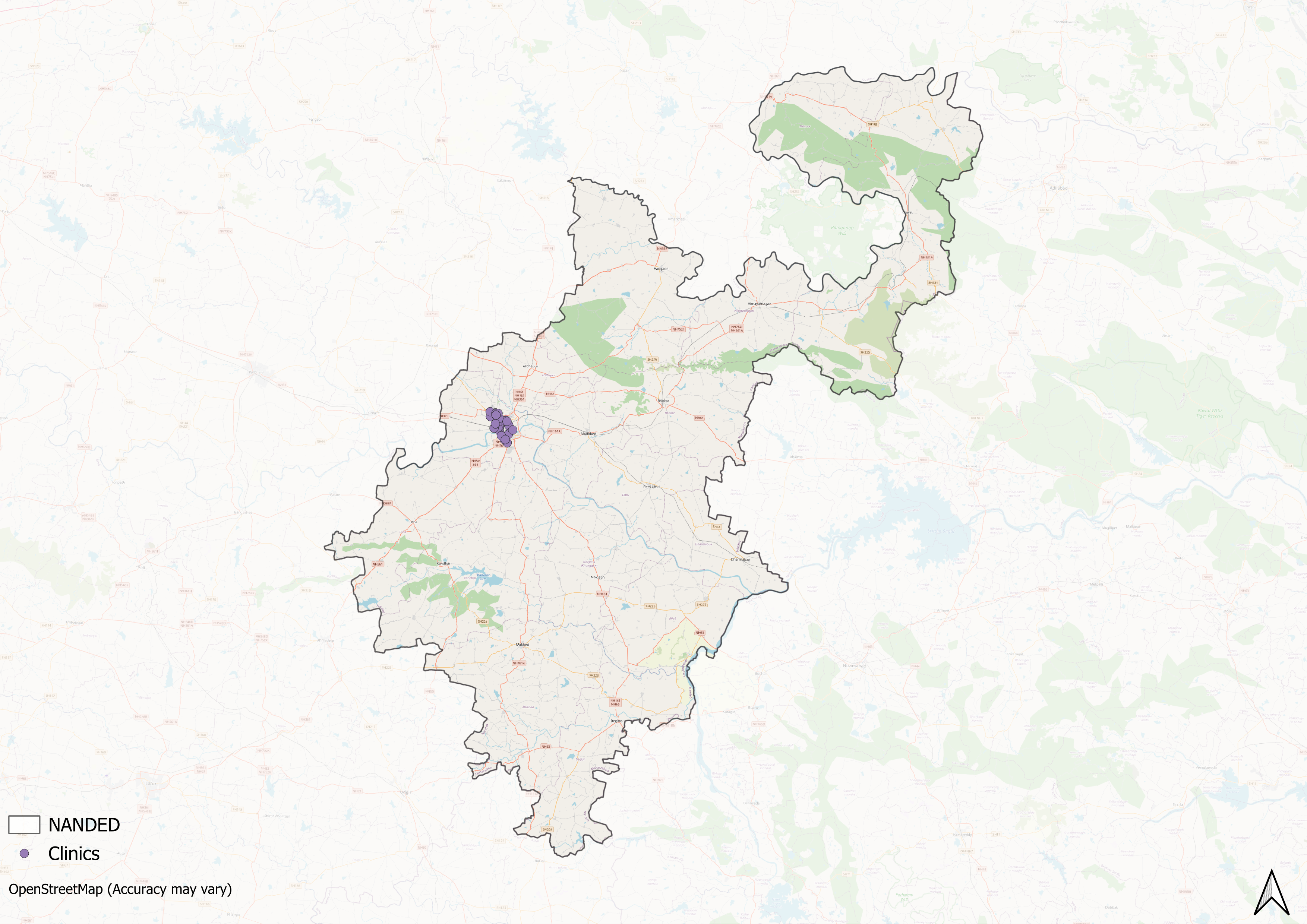
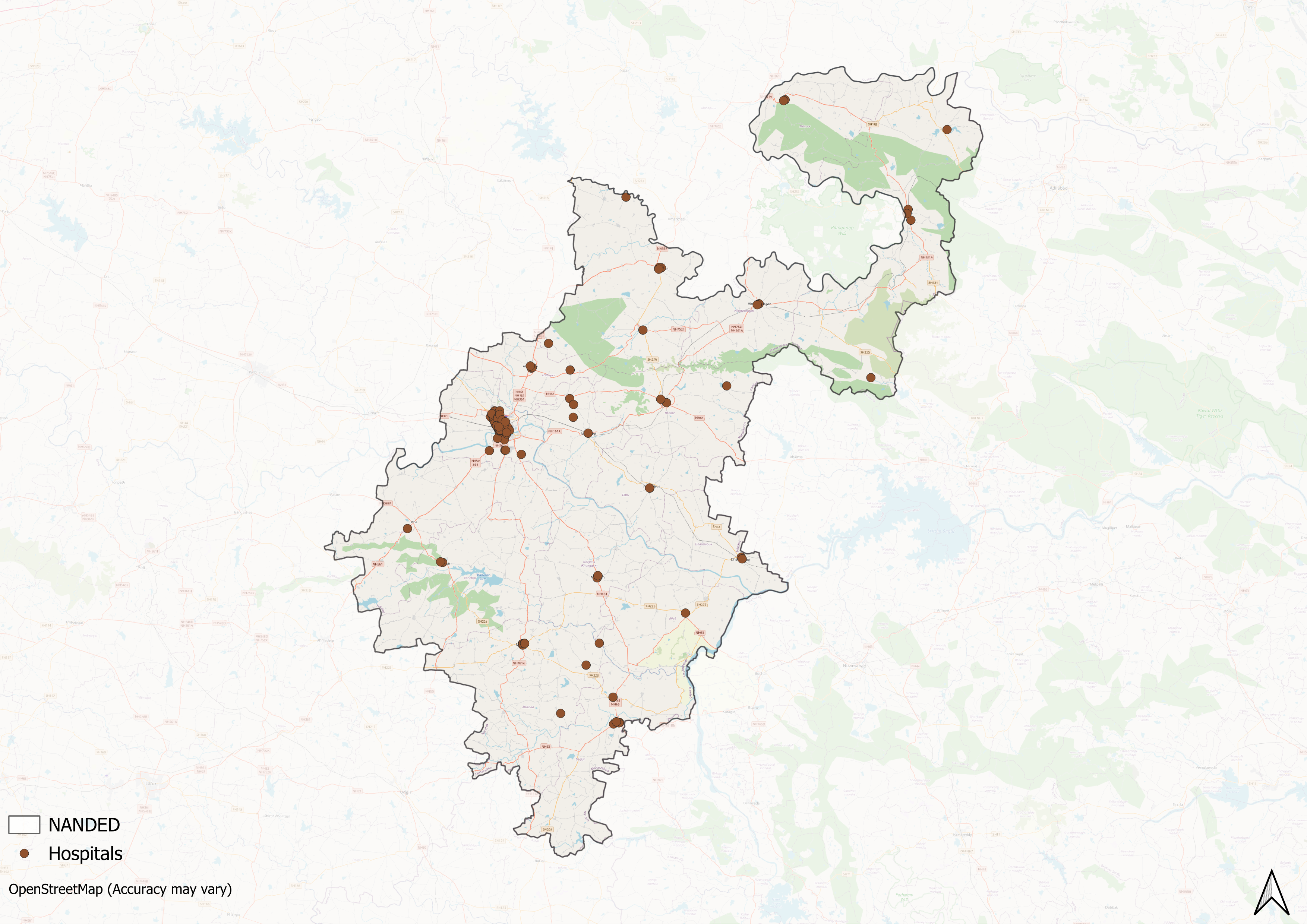
Supporting this structure is a network of Accredited Social Health Activists (ASHAs) who, as described by the National Health Mission, serve as “an interface between the community and the public health system.” Over the years, this structure has been shaped and refined by national health policies and reforms, with the broader goal of expanding access and achieving universal health coverage for both urban and rural communities.
In the 20th century, two major institutions influenced the district’s healthcare landscape: the General Hospital, which provided allopathic medical care for a wide range of health needs, and the Ayurvedic Hospital, established in 1956. The Ayurvedic Hospital is one of the oldest of its kind in Maharashtra and is known for its 100-acre herbal garden, which supplies medicinal plants used in treatment and reflects the region’s strong connection to traditional Indian medicine.
![Government Ayurvedic College and Hospital, Nanded[1]](/media/statistic/images/maharashtra/nanded/health/government-ayurvedic-college-and-hospital-nan_jtXdzrD.png)
Over time, the public health infrastructure in Nanded expanded further, alongside the gradual emergence of private hospitals and clinics through the 20th and 21st centuries. Many of these private facilities were established by local trusts, NGOs, and community groups, adding capacity alongside government institutions.
One of the district’s major public healthcare centres is the Dr. Shankarrao Chavan Government Medical College and Hospital (SCGMC) in Vishnupuri, established in 1988 by Shankarrao Chavan, then Chief Minister of Maharashtra. Notably, it operates a 600-bed hospital that serves not only Nanded but also neighbouring districts such as Parbhani, Hingoli, Yavatmal, and parts of Telangana.
Although the hospital has advanced infrastructure and a large capacity, it continues to face challenges related to overcrowding and limited resources, which have affected cleanliness and overall service quality. These issues became particularly evident in October 2023, when 35 deaths were reported within 48 hours. The incident highlighted the severe pressure on medical staff and facilities and pointed to the wider need for better management and resource allocation to strengthen healthcare in the region.
Graphs
Healthcare Facilities and Services
Morbidity and Mortality
Maternal and Newborn Health
Family Planning
Immunization
Nutrition
Sources
British Government of India. 1908. Nizam's Dominions District Gazetteer: Nanded. Government of India Press, Calcutta.
Dr. Shankarrao Chavan Government Medical College, Nanded. "Overview." Dr. SC GMC Nanded.https://drscgmcnanded.in/overview.php
Government Arts College, Nanded. "About Us." GAC Nanded.https://gacnanded.com/
Moudgil, Manmohan. 2023. "Nanded Hospital Deaths Expose Maharashtra’s Healthcare Crisis." Frontline, The Hindu.https://frontline.thehindu.com/news/nanded-h…
Sharma, P., & Deshmukh, A. 2014. "Traditional Healing Practices in Nanded: An Ethnobotanical Study." Vol. 4, no. 5.International Journal of Ayurveda and Herbal Medicine.https://interscience.org.uk/v4-i5/6%20ijahm.…
Last updated on 26 July 2025. Help us improve the information on this page by clicking on suggest edits or writing to us.